Which Explanation Best Explains The Role Of Enzymes As Catalysts In Living Systems?
Which explanation best explains the role of enzymes as catalysts in living systems?. The role of enzymes in the fermentation process has been known for less than two hundred years. Aspirin is a covalent modifier of enzymes involved in the inflammatory response. Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions without getting used up in the process.
No enzymes are catalyst of biological reactions meaning they speed up reactions of altering and affecting molecules in our bodies but it does not have to be breakdown. Enzymes or biological catalysts allow reactions that are necessary to sustain life proceed relatively quickly at the normal environmental temperatures. IN DNA replication they unwind DNA or synthesize DNA.
Which explanation best explains the role of enzymes as catalysts in living systems. Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions. An enzyme is a type of protein found within a cell.
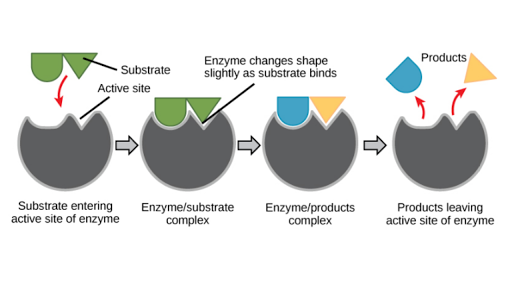
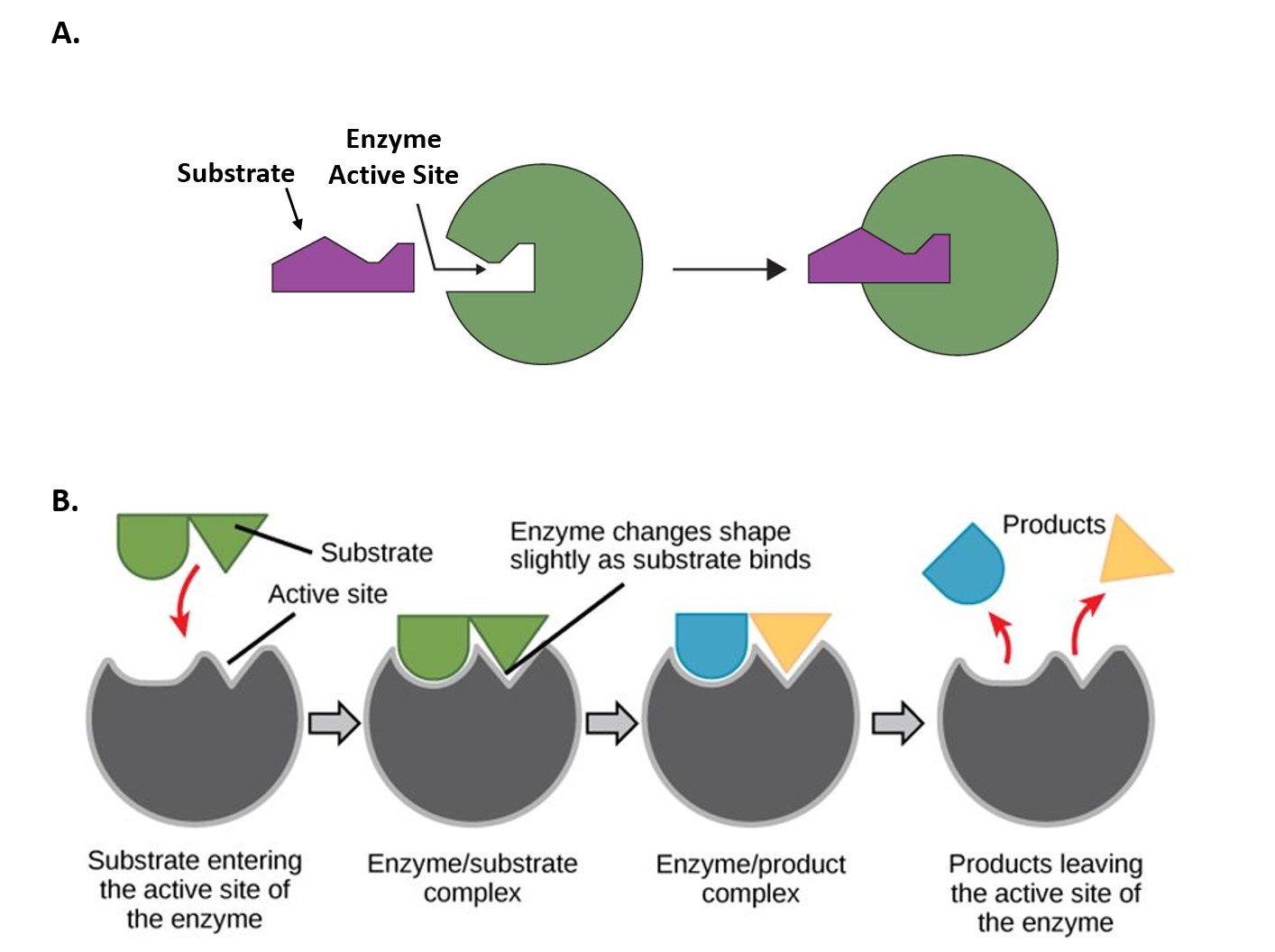
Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze chemical reaction by first binding to molecultes and then linging them up in ways that increase the probability of the molecules exhanging atoms when they collide. Enzymes are biological catalysts Enzymes are the catalysts involved in biological chemical reactions.
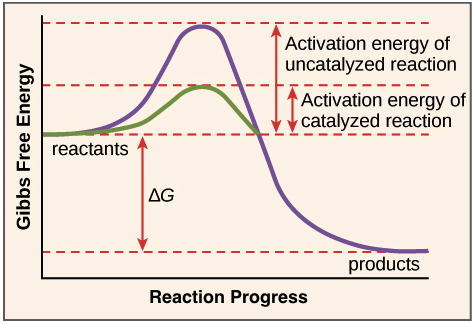
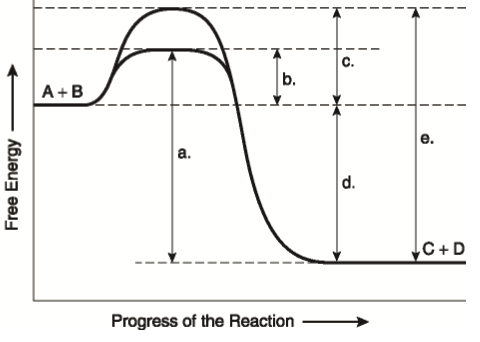
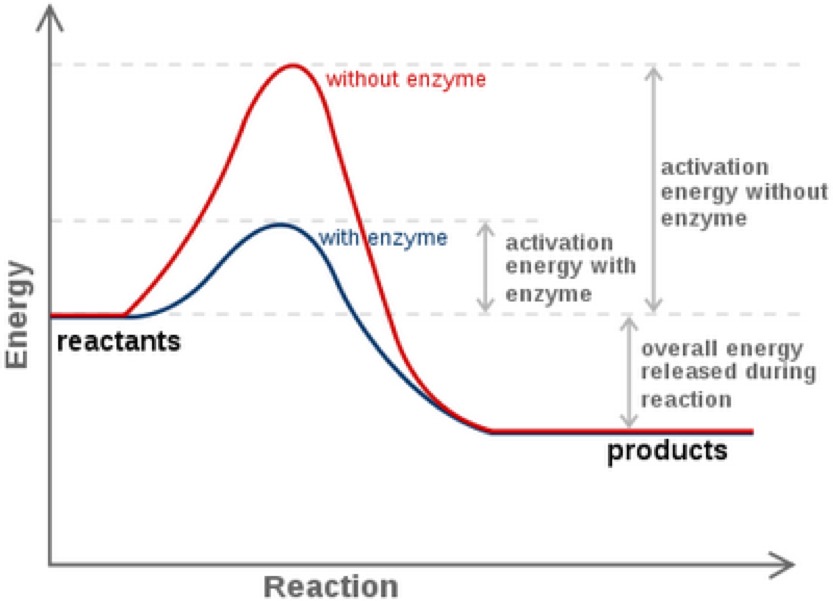
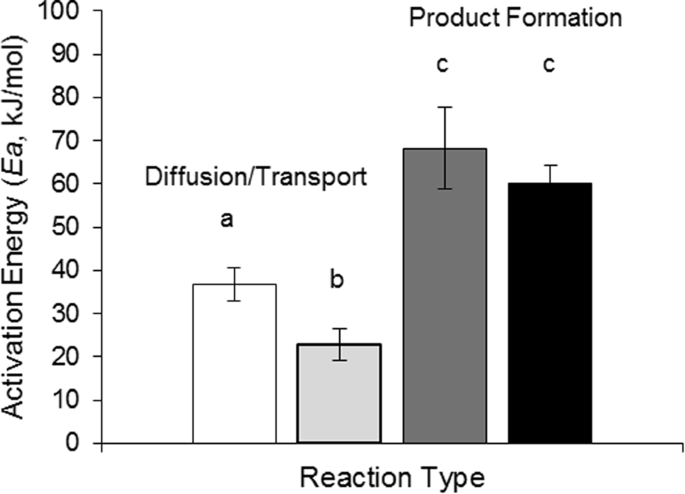
They are specific for their substrate. The fact that they arent changed by participating in a reaction distinguishes catalysts from substrates which are the reactants on which catalysts work. Catalysts lower the activation energy for reactions.
The digestive system enzymes help the body break down larger complex molecules into smaller molecules such as glucose so that the body can use them as. Enzymes Are Catalysts A catalyst is a chemical that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being changed by the reaction. Helicase and DNA POlymerase.
Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions without getting used up in the process. They actually speed up the rate of a chemical reaction to help support life.
Because the cell wall is not able to protect the bacterial cell the organism bursts.
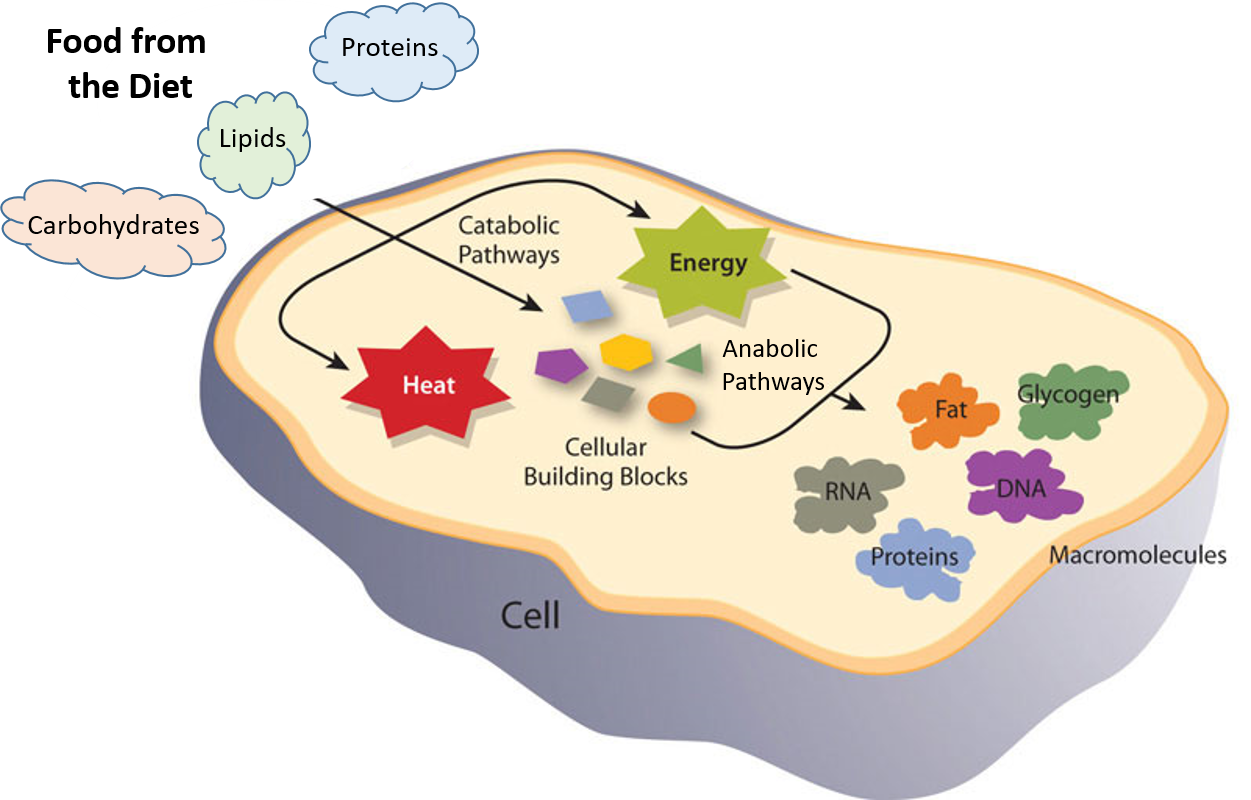
Digestive enzymes are known to break down molecules but here are some other functions. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells and RNAs are capable of catalyzing some reactions most biological reactions are catalyzed by proteinsBut the. Helicase and DNA POlymerase. Enzymes act as catalysts. Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions by. They do not get consumed in the chemical reactions that they accelerate. IN DNA replication they unwind DNA or synthesize DNA. The enzymes Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for specific biochemical processes. The digestive system enzymes help the body break down larger complex molecules into smaller molecules such as glucose so that the body can use them as.
Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions without getting used up in the process. Aspirin is a covalent modifier of enzymes involved in the inflammatory response. Enzymes are needed for metabolic pathways in the body respiration digestion and other important life. An enzyme is a type of protein found within a cell. Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up reactions. They are the gnomes inside each one of us that take molecules like nucleotides and align them together to create DNA or amino acids to make proteins to name two of thousands of such functions. The fact that they arent changed by participating in a reaction distinguishes catalysts from substrates which are the reactants on which catalysts work.




























Post a Comment for "Which Explanation Best Explains The Role Of Enzymes As Catalysts In Living Systems?"